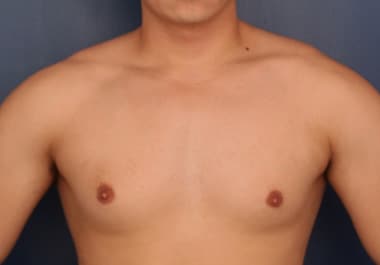
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue in males. This condition occurs due to an imbalance between the hormones testosterone and estrogen. While often harmless, gynecomastia can cause emotional distress and physical discomfort, leading many to question the root causes and seek solutions. This article delves into whether gynecomastia is linked to testosterone levels, exploring the hormonal interplay and other contributing factors.
The Role of Hormones in Male Physiology:
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, is responsible for developing male characteristics such as muscle mass, deep voice, and body hair. Estrogen, often associated with female physiology, is present in males but in much smaller amounts. In a healthy male, testosterone usually suppresses the effects of estrogen. However, when the balance between these hormones shifts either due to reduced testosterone or increased estrogen levels conditions like Gynecomastia Dubai can develop.
Hormonal Imbalance and Gynecomastia:
Gynecomastia typically arises when estrogen levels overshadow testosterone levels. This imbalance can result from several factors, including:
- Natural Hormonal Fluctuations:
Gynecomastia is common during certain life stages, such as infancy, puberty, and older adulthood. During puberty, rapid hormonal changes may temporarily increase estrogen relative to testosterone, leading to breast tissue enlargement. - Testosterone Deficiency:
Low testosterone levels, medically termed hypogonadism, can directly contribute to gynecomastia. Causes of hypogonadism include aging, testicular injury, or certain medical conditions like Klinefelter syndrome. - Increased Estrogen Levels:
Higher-than-normal estrogen levels, due to tumors, obesity, or hormonal therapies, can create the conditions necessary for gynecomastia to develop.
Lifestyle Factors Impacting Hormonal Balance:
While hormonal imbalances are the primary cause of gynecomastia, lifestyle factors can also influence testosterone and estrogen levels.
- Obesity:
Fat cells can convert testosterone into estrogen through a process called aromatization. Excess body fat increases estrogen levels, tipping the hormonal scale and potentially leading to gynecomastia. - Medications:
Certain medications, including anabolic steroids, anti-androgens, and some antidepressants, can disrupt hormonal balance and trigger gynecomastia. - Substance Abuse:
The use of alcohol, marijuana, and illicit drugs can interfere with testosterone production, contributing to gynecomastia. - Diet and Exercise:
A sedentary lifestyle and poor diet can lower testosterone levels. Conversely, regular exercise and a balanced diet rich in zinc and healthy fats can help maintain optimal hormone levels.
How Testosterone Levels Affect Gynecomastia:
A deficiency in testosterone or a disruption in its normal production can significantly increase the risk of developing gynecomastia.
- Andropause in Older Men:
As men age, testosterone production naturally declines, a phenomenon often referred to as andropause. This age-related hormonal shift can result in gynecomastia, especially when paired with weight gain and reduced physical activity. - Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT):
Ironically, while TRT is often used to treat low testosterone, it can sometimes exacerbate gynecomastia. This occurs when excess testosterone is converted into estrogen, leading to an imbalance.
Diagnosing the Underlying Cause of Gynecomastia:
If gynecomastia is suspected, medical evaluation is crucial to identify its cause. Diagnostic steps typically include:
Medical History and Physical Examination:
Physicians will assess lifestyle factors, medication usage, and symptoms to determine potential causes.
Blood Tests:
Hormonal levels, including testosterone, estrogen, and other markers, are measured to identify imbalances.
Imaging Tests:
In some cases, imaging studies like ultrasound or mammography may be required to rule out other conditions, such as male breast cancer.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia:
The treatment for gynecomastia depends on its underlying cause and severity. Options include:
Addressing Hormonal Imbalances:
Medications:
Drugs like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) or aromatase inhibitors may be prescribed to reduce estrogen levels.
Hormone Therapy Adjustments:
For men undergoing TRT, adjustments to therapy may help restore balance.
Lifestyle Changes:
Weight Management:
Losing weight can help reduce estrogen levels and improve hormonal balance.
Exercise and Nutrition:
Resistance training and a diet rich in testosterone-supporting nutrients can promote healthy hormone levels.
Surgical Intervention:
Liposuction:
Removes excess fatty tissue from the breast area.
Mastectomy:
Removes glandular breast tissue, often recommended for severe cases.
Psychological Support:
Emotional and psychological support is essential for men coping with Gynecomastia in Dubai, as the condition often impacts self-esteem.
Can Gynecomastia Be Prevented?
While some cases of gynecomastia are unavoidable, particularly those linked to puberty or aging, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid anabolic steroids and recreational drugs.
- Be cautious with medications known to affect hormone levels.
- Engage in regular exercise to support hormonal health.
Conclusion:
Gynecomastia is closely linked to testosterone and estrogen levels. A disruption in the balance between these hormones can result in the development of the condition. While low testosterone is a common contributing factor, increased estrogen levels and lifestyle factors also play significant roles. By understanding the hormonal dynamics of gynecomastia, individuals can seek appropriate treatment, make lifestyle adjustments, and consult healthcare providers to address the condition effectively.