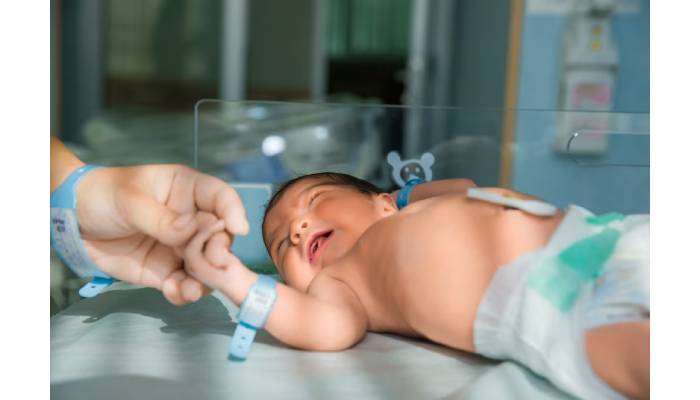
Collecting newborn stem cells at birth is really important for a variety of reasons. These stem cells, especially those found in umbilical cord blood, are valuable because they can turn into different types of blood cells. They are used to treat serious conditions like leukemia and sickle cell anemia, and they usually face less rejection when used for transplants compared to adult stem cells. The process itself is non-invasive and safe for both mother and baby. Families can bank these stem cells for future medical needs, which can be a wise choice considering the ongoing research into their potential uses in regenerative medicine.
1. Understanding Newborn Stem Cells and Their Sources
The newborn stem cell mainly comes from umbilical cord blood, which is collected right after birth. This blood is rich in hematopoietic stem cells, the type that can develop into various blood cells. These stem cells have a unique capability to treat serious health conditions like leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle cell anemia. Since they’re collected from newborns, there’s a lower chance of rejection when used for transplants, making them a more compatible option for patients. The collection process is non-invasive and poses no risk to either the mother or the baby, which is a significant advantage. Additionally, families can store these stem cells for future medical needs, creating a potential resource for siblings or relatives who may face health challenges later in life. As more research unfolds, the possibilities for using these stem cells in regenerative medicine continue to expand.

2. How Stem Cells Help Treat Serious Diseases?
Newborn stem cells, particularly those derived from umbilical cord blood, play a vital role in treating serious diseases. They are a primary source of hematopoietic stem cells, which can evolve into various types of blood cells. Conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle cell anemia can be addressed through stem cell transplants using these cells. For example, children suffering from leukemia often find hope in cord blood transplants, which can restore healthy blood cell production.
One of the significant advantages of using newborn stem cells is the lower risk of rejection. Unlike stem cells from adult donors, which may be recognized as foreign by the recipient’s immune system, cord blood stem cells tend to be more compatible, reducing the chances of complications during transplantation. This compatibility is especially crucial for patients who may not have a matched donor available.
Moreover, the potential of newborn stem cells extends beyond immediate treatments for blood-related disorders. Researchers are actively investigating their use in regenerative medicine, exploring applications for conditions like cerebral palsy and certain genetic disorders. This ongoing research holds promise for developing innovative therapies that could transform the landscape of medical treatment.
Overall, the collection of newborn stem cells at birth not only provides immediate therapeutic options but also opens doors to future medical advancements, making it an essential consideration for families.
3. The Benefits of Lower Rejection Rates
One of the significant advantages of collecting newborn stem cells, particularly from umbilical cord blood, is the lower risk of rejection when used in transplants. Unlike adult stem cells, which may face challenges in compatibility due to the recipient’s immune system, newborn stem cells are often more universally accepted. This is largely due to their unique properties and the fact that they are less mature, which reduces the likelihood of an immune response. For instance, when a child requires a stem cell transplant to treat leukemia, using their own cord blood can significantly increase the chances of a successful outcome. This not only offers peace of mind for families but also enhances the effectiveness of treatments, making newborn stem cells a promising option in medical therapies.
4. Exploring Regenerative Medicine Potential
The potential of newborn stem cells in regenerative medicine is a captivating area of research. Scientists are exploring how these cells, harvested from umbilical cord blood, might aid in repairing damaged tissues and organs. For instance, there are ongoing studies investigating the use of these stem cells for conditions like cerebral palsy, where traditional treatments may fall short. By tapping into the natural regenerative properties of these cells, researchers hope to develop therapies that could help restore functionality and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. Additionally, conditions such as autism and various degenerative diseases are also being examined for their potential treatment through these innovative approaches. As our understanding grows, the possibilities for utilizing newborn stem cells in regenerative medicine appear increasingly promising.
5. Safe and Non-Invasive Collection Process
The collection of newborn stem cells, particularly from umbilical cord blood, is a remarkably safe and non-invasive process. This procedure typically occurs right after the baby is born and does not interfere with the delivery or the health of the mother and newborn. Medical professionals use a sterile technique to collect the cord blood, which is the blood remaining in the umbilical cord and placenta after birth. Since it involves no surgical procedure, there are no risks associated with the collection for either the mother or the baby.
For parents, this means they can opt for this potentially life-saving resource without the stress of invasive procedures. The entire process usually takes only a few minutes and can be performed in a routine hospital setting. The simplicity of this collection method, paired with its safety, makes it an appealing choice for many families. Additionally, it is a one-time opportunity; once the umbilical cord is cut, the chance to collect stem cells is gone. Thus, ensuring that this non-invasive method is utilized can provide invaluable benefits for future medical needs.
- Collection occurs immediately after birth.
- Umbilical cord blood is collected without harming the mother or baby.
- The procedure typically takes just a few minutes.
- Does not require any surgical intervention.
- Safe for both the newborn and the mother.
- No anesthesia is used during collection.
- The process is overseen by trained medical professionals.
6. Family Banking for Future Health Needs
Family banking of newborn stem cells offers a unique opportunity for future health needs. When parents choose to store their baby’s cord blood, they are essentially creating a personal health resource that could benefit not just the newborn but also siblings or other family members. For example, if a sibling later develops a condition like leukemia, the stored stem cells could be a match, providing a potential lifesaving treatment option. This foresight can be particularly valuable in families with a history of genetic disorders or illnesses that might require stem cell intervention. The peace of mind that comes from knowing you have a resource available for unforeseen health challenges is a compelling reason for many families to consider cord blood banking.
7. Growing Awareness and Ongoing Research
As more families learn about the potential uses of newborn stem cells, the interest in collecting and storing these cells is steadily increasing. Research is expanding into the many applications of stem cells, revealing promising possibilities for treating an array of conditions beyond traditional blood disorders. For instance, recent studies are exploring how these cells could be used in the treatment of neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy and autism. This ongoing research is crucial, as it not only enhances our understanding of stem cell capabilities but also opens doors for innovative therapies that could improve the quality of life for many children. Additionally, with advancements in technology, the extraction and storage methods for these stem cells are becoming more efficient, making it easier for families to consider this option. The growing body of evidence supporting the benefits of newborn stem cells is likely to influence medical practices and guidelines in the coming years.
8. Evaluating the Costs of Cord Blood Storage
When considering the collection of newborn stem cells, one important aspect to evaluate is the cost of cord blood storage. Families often face a range of fees associated with the initial collection and the ongoing annual storage. These costs can vary significantly depending on the facility and the services offered. For instance, the initial processing fee might range from $1,000 to $2,000, with annual storage fees typically around $100 to $200. While these figures might seem substantial, it is essential to weigh them against the potential health benefits. The stored cord blood could be invaluable in treating various conditions that may arise later in life for the child or even siblings. Additionally, as advancements in medical technology continue to accelerate, the potential uses of stored stem cells could increase, potentially making this investment even more worthwhile. Parents may also want to consider the options of public versus private banking; public banking is often free but does not guarantee the availability of the stem cells for personal use in the future. Ultimately, evaluating costs involves not only looking at the financial aspect but also considering the long-term health implications for the family.
9. Advancements in Stem Cell Technology
Recent advancements in stem cell technology are paving the way for exciting possibilities in both treatment and research. Scientists are making strides in understanding how to maximize the potential of newborn stem cells, particularly those derived from umbilical cord blood. For instance, improved techniques in cell processing and storage are enhancing the viability and functionality of these cells for future use.
Moreover, innovative methods such as gene editing are being explored to correct genetic defects in stem cells, potentially allowing for tailored therapies that could address specific health challenges. This could lead to breakthroughs in treating genetic disorders that were once thought to be untreatable.
On the research front, new studies are investigating how these stem cells can be utilized in combination with other therapies, such as immunotherapy for cancer treatment. As technology continues to evolve, the scope of what can be achieved with newborn stem cells expands, offering hope for more effective and personalized medical interventions.
10. Ethical Advantages of Cord Blood Collection
Collecting cord blood is considered ethically favorable compared to other stem cell sources, particularly embryonic stem cells. The practice involves no destruction of embryos, which is a significant ethical concern for many. Instead, cord blood is collected from the umbilical cord after birth, a process that poses no harm to the mother or newborn. This non-invasive method aligns with the growing sentiment in society supporting procedures that respect life and promote health without ethical dilemmas. Additionally, the potential use of these stem cells for treating diseases not only benefits the child but can also provide life-saving options for family members, reinforcing the notion of familial care and responsibility. As medical advancements continue, the ethical acceptance of cord blood collection is likely to grow, paving the way for wider usage in treatments and research.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are newborn stem cells, and why are they important?
Newborn stem cells are special cells found in the umbilical cord and placenta. They are important because they can develop into many types of cells in the body, helping to treat various medical conditions in the future.
2. How is the process of collecting stem cells done at birth?
The process involves clipping the umbilical cord after the baby is born and collecting the blood from the cord. It’s a simple and safe procedure that doesn’t hurt the mother or the baby.
3. What conditions can newborn stem cells potentially help treat?
Newborn stem cells can help with several health issues, including certain cancers, blood disorders, and immune system problems. They have great potential for future medical treatments.
4. Is it safe to collect stem cells during birth?
Yes, collecting stem cells is very safe. The process is quick and does not interfere with the birth or the well-being of the mother and baby.
5. Can parents choose to collect stem cells after the baby is born?
Yes, parents can decide to collect stem cells after birth, but it’s important to plan ahead and talk to your healthcare provider about it before the birth.
TL;DR Collecting newborn stem cells from umbilical cord blood at birth is crucial for future medical treatments. These stem cells are vital for treating diseases like leukemia and have lower rejection rates in transplants. The non-invasive collection process ensures safety for both mother and baby, while family banking offers long-term health benefits. As awareness grows, ongoing research and advancements in stem cell technology promise exciting potential in regenerative medicine, all with fewer ethical concerns compared to other sources.